MapReduce原理
在运行一个 mapreduce 计算任务时候,任务过程被分为两个阶段:map 阶段和 reduce 阶段,每个阶段都是用键值对(key/value)作为输入(input)和输出(output)。而程序员要做的就是定义好这两个阶段的函数:map 函数和 reduce 函数。
MapReduce的HelloWorld——WordCount
/**
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one
* or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
* distributed with this work for additional information
* regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file
* to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
* "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
* with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.apache.hadoop.examples;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.GenericOptionsParser;
public class WordCount {
public static class TokenizerMapper
extends Mapper<Object, Text, Text, IntWritable>{
private final static IntWritable one = new IntWritable(1);
private Text word = new Text();
public void map(Object key, Text value, Context context
) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
StringTokenizer itr = new StringTokenizer(value.toString());
while (itr.hasMoreTokens()) {
word.set(itr.nextToken());
context.write(word, one);
}
}
}
public static class IntSumReducer
extends Reducer<Text,IntWritable,Text,IntWritable> {
private IntWritable result = new IntWritable();
public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values,
Context context
) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
int sum = 0;
for (IntWritable val : values) {
sum += val.get();
}
result.set(sum);
context.write(key, result);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
String[] otherArgs = new GenericOptionsParser(conf, args).getRemainingArgs();
if (otherArgs.length != 2) {
System.err.println("Usage: wordcount <in> <out>");
System.exit(2);
}
Job job = new Job(conf, "word count");
job.setJarByClass(WordCount.class);
job.setMapperClass(TokenizerMapper.class);
job.setCombinerClass(IntSumReducer.class);
job.setReducerClass(IntSumReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[1]));
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
}
}
MapReduce运行机制
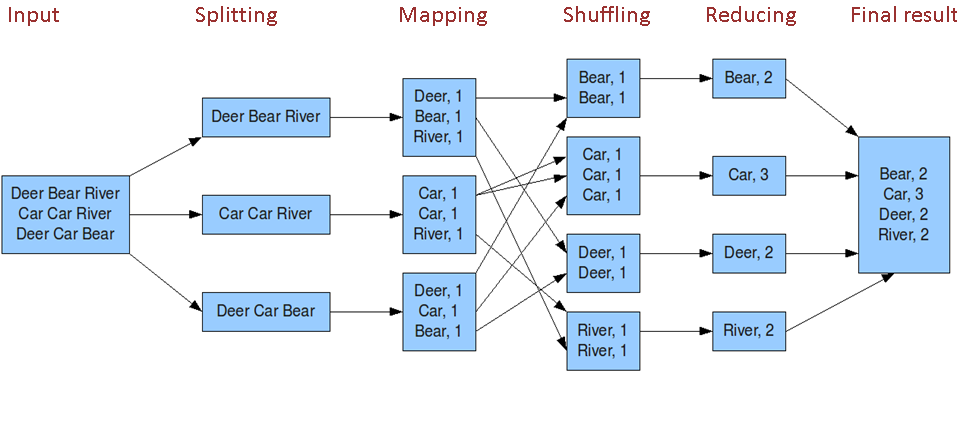
MapReduce程序按时间顺序分为几个阶段:输入分片(split)、map 阶段、combiner 阶段、shuffle 阶段和 reduce 阶段。
- split:在进行 map 计算之前,mapreduce 会根据输入文件计算输入分片(input split),每个输入分片(input split)针对一个 map 任务,输入分片(input split)存储的并非数据本身,而是一个分片长度和一个记录数据的位置的数组,输入分片(input split)往往和 hdfs 的 block(块)关系很密切,假如我们设定 hdfs 的块的大小是 64mb,如果我们输入有三个文件,大小分别是 3mb、65mb 和 127mb,那么 mapreduce 会把 3mb 文件分为一个输入分片(input split),65mb 则是两个输入分片(input split)而 127mb 也是两个输入分片(input split),换句话说我们如果在 map 计算前做输入分片调整,例如合并小文件,那么就会有 5 个 map 任务将执行,而且每个 map 执行的数据大小不均,这个也是 mapreduce 优化计算的一个关键点。
- map:就是程序员编写好的 map 函数了,因此 map 函数效率相对好控制,而且一般 map 操作都是本地化操作也就是在数据存储节点上进行 。
- combiner:combiner 阶段是程序员可以选择的,combiner 其实也是一种 reduce 操作,因此我们看见 WordCount 类里是用 reduce 进行加载的。Combiner 是一个本地化的 reduce 操作,它是 map 运算的后续操作,主要是在 map 计算出中间文件前做一个简单的合并重复 key 值的操作,例如我们对文件里的单词频率做统计,map 计算时候如果碰到一个 hadoop 的单词就会记录为 1,但是这篇文章里 hadoop 可能会出现 n 多次,那么 map 输出文件冗余就会很多,因此在 reduce 计算前对相同的 key 做一个合并操作,那么文件会变小,这样就提高了宽带的传输效率,毕竟 hadoop 计算力宽带资源往往是计算的瓶颈也是最为宝贵的资源,但是 combiner 操作是有风险的,使用它的原则是 combiner 的输入不会影响到 reduce 计算的最终输入,例如:如果计算只是求总数,最大值,最小值可以使用 combiner,但是做平均值计算使用 combiner 的话,最终的 reduce 计算结果就会出错。
- shuffle:将 map 的输出作为 reduce 的输入的过程就是 shuffle 了,这个是 mapreduce 优化的重点地方。这里我不讲怎么优化 shuffle 阶段,讲讲 shuffle 阶段的原理,因为大部分的书籍里都没讲清楚 shuffle 阶段。Shuffle 一开始就是 map 阶段做输出操作,一般 mapreduce 计算的都是海量数据,map 输出时候不可能把所有文件都放到内存操作,因此 map 写入磁盘的过程十分的复杂,更何况 map 输出时候要对结果进行排序,内存开销是很大的,map 在做输出时候会在内存里开启一个环形内存缓冲区,这个缓冲区专门用来输出的,默认大小是 100mb,并且在配置文件里为这个缓冲区设定了一个阀值,默认是 0.80(这个大小和阀值都是可以在配置文件里进行配置的),同时 map 还会为输出操作启动一个守护线程,如果缓冲区的内存达到了阀值的 80% 时候,这个守护线程就会把内容写到磁盘上,这个过程叫 spill,另外的 20% 内存可以继续写入要写进磁盘的数据,写入磁盘和写入内存操作是互不干扰的,如果缓存区被撑满了,那么 map 就会阻塞写入内存的操作,让写入磁盘操作完成后再继续执行写入内存操作,前面我讲到写入磁盘前会有个排序操作,这个是在写入磁盘操作时候进行,不是在写入内存时候进行的,如果我们定义了 combiner 函数,那么排序前还会执行 combiner 操作。每次 spill 操作也就是写入磁盘操作时候就会写一个溢出文件,也就是说在做 map 输出有几次 spill 就会产生多少个溢出文件,等 map 输出全部做完后,map 会合并这些输出文件。这个过程里还会有一个 Partitioner 操作,对于这个操作很多人都很迷糊,其实 Partitioner 操作和 map 阶段的输入分片(Input split)很像,一个 Partitioner 对应一个 reduce 作业,如果我们 mapreduce 操作只有一个 reduce 操作,那么 Partitioner 就只有一个,如果我们有多个 reduce 操作,那么 Partitioner 对应的就会有多个,Partitioner 因此就是 reduce 的输入分片,这个程序员可以编程控制,主要是根据实际 key 和 value 的值,根据实际业务类型或者为了更好的 reduce 负载均衡要求进行,这是提高 reduce 效率的一个关键所在。到了 reduce 阶段就是合并 map 输出文件了,Partitioner 会找到对应的 map 输出文件,然后进行复制操作,复制操作时 reduce 会开启几个复制线程,这些线程默认个数是 5 个,程序员也可以在配置文件更改复制线程的个数,这个复制过程和 map 写入磁盘过程类似,也有阀值和内存大小,阀值一样可以在配置文件里配置,而内存大小是直接使用 reduce 的 tasktracker 的内存大小,复制时候 reduce 还会进行排序操作和合并文件操作,这些操作完了就会进行 reduce 计算了。
- reduce:和 map 函数一样也是程序员编写的,最终结果是存储在 hdfs 上的。